Solar power. How to use its energy
About the sun:
Solar Power is energy obtained by the sun in the form of light.
( When you are at the beach, you feel the sun as heat energy, but heat energy can’t travel through space. It is just light energy that gives the hot feeling)
The sun is 150 million km from the earth and is 5 billion years old ( so don´t worry about sun death ).
The temperature of the sun ranges from 6000 degrees Celsius at its surface to 10 million degrees Celsius at its centre.
It takes about 8 minutes for the light energy to touch the earth. The sun is a star made up of hydrogen and helium gas and it radiates an enormous amount of energy every second and it is clean.
If we could “catch ” the amount of solar energy that arrive every single day to earth and convert it into electrical energy, it would be enough to supply our energy needs for up to one a year.
Solar Cells
Originally developed in order to provide electrical energy for space satellites, photovoltaic energy uses photoelectric cells that convert light into electricity. 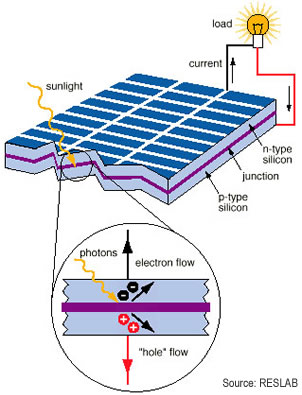
Solar photovoltaic power or PV takes advantage of the photovoltaic effect in which a solar cell converts sunlight into electricity.
In 1839, nineteen-year-old Edmund Becquerel, while experimenting with an electrolytic cell made up of two metal electrodes, found that certain materials would produce small amounts of electric current when exposed to light.
In Sunlight there is a particle called a photons. When photons strike a pv (solar cell), they may be absorbed by a atom, so that the energy of the photon is transferred to the electron of the atom that receives that energy.
In a modem cell, the materials used for the solar cell are semiconductors.
There are two types of semiconductor: the N-type (in which there are a lot of nearly free electrons ) and the P-type ( in which there are a lot of “Holes”). It is called a hole when an electron has left its place, so in P-type semiconductor, there is a positive charge.
If a photon strike a N-type semiconductor, the electron can escape from its normal position. If the electron is free to move, and as it has a negative charge, it will try to catch a positive charge. The positive charges are located in the P-type semiconductor ( below in the solar cell- see drawing ) and although they are attracted by them, it is impossible for electrons to pass the junction ( violet material ) as it is an insulator component. What can they do then?
The only way to find a Hole is by going out from the solar cell, passing through the load ( a bulb in this case ) and taking the wire toward the P-Type semiconductor. Now, we have electricity, clean, safe, non-polluting and getting cheaper every day.
SOLAR WATER HEATING.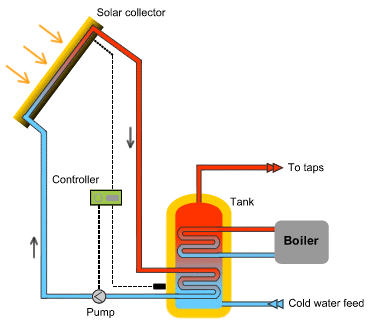
The diagram shown on the right illustrates a simple water heating circuit.
The solar collector contains two independent circuits. An oil circuit in a closed system comprises a solar collector, the tubes and a small pump ( needed to move hot oil through the circuit ) and a U-tube heat exchanger in the water tank.
The cold oil is moved by the pump, collects heat energy in the solar collector, goes to the u-tube heat exchanger and transfers some of its heat to the water in the tank.
The second circuit, starts in a cold water feed which fills up the thank and pick up energy from the U-tube heat exchanger. Once the water is warm it can be used in a tap water circuit.
If we want to produce electricity from the sun, the best way is by a thermal solar plant
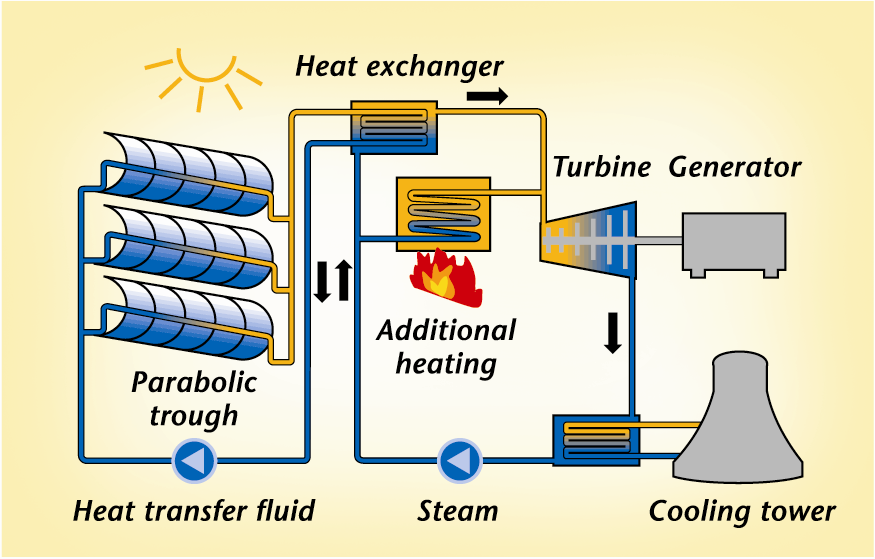
In an industrial Solar plant, an array of mirrors acts as a parabolic reflector concentrating solar energy onto a focal point ( where the tube with a thermal liquid is installed. The temperature of the heat transfer fluid, at the focal point, may reach 3,000 ºC. This heat is used to give energy to the water circuit inside a Heat exchanger.
Water changes into stream and moves a turbine whose axle moves the generator, producing electricity.
Steam water is change into liquid and pushed again to the heat exchanger

San Lucar la Mayor Solar plant is the pride of Abengoa ( a Spanish technology company ). This plant generates 24.3 GWh per year of clean energy which is enough to supply 6000 households.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES
- Once solar panels are installed, they produce energy without generating pollution.
- They operate with little maintenance .
- Competitive where grid connection or fuel transport is difficult. For example: island communities, remote locations, etc.
- A solar panel saves approximately 1kg of carbon dioxide per kWh. The below illustration below tell you a bit more
-

DISADVANTAGES- Solar energy systems, of course, do not work at night.
- Nowadays solar cells are costly.
- For larger applications, a lot of land is needed
