DNS and Data Security.
A big problem with the Internet is that data is transmitted using telephone technology, which means unauthorised users can intercept the data relatively easily. Which is a bit of a pain, really.
On-Line Shopping uses Encryption Software
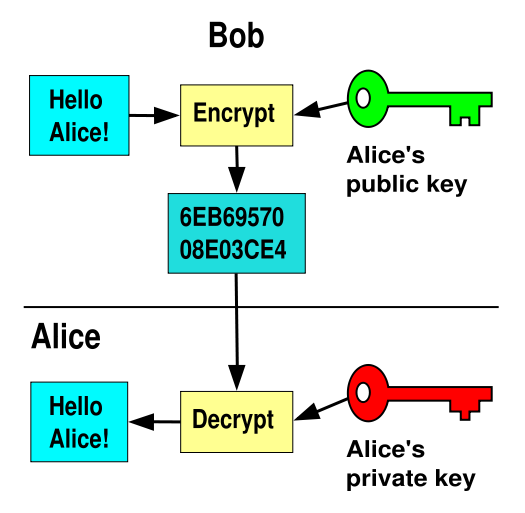 1) On-line shopping or e-commerce has got much more popular recently. 2) The basic idea is that the retailer puts details of their products on a web site. Customers can put the stuff they want into an electronic basket (by clicking on a button). They then pay using a credit card, and the goods are delivered soon after. 3) Some people don’t like on-line shopping because they’re worried that their credit card details might be intercepted and used to make unauthorised purchases. Encryption software can reduce this risk. 4) Sensitive information — like credit card details — is encrypted by the web site into a code which can only be decoded with the right software and a special password called a key. In theory, only the retailer’s web site can access the information, so even if someone intercepts the transmission, they won’t be able to use the data.
1) On-line shopping or e-commerce has got much more popular recently. 2) The basic idea is that the retailer puts details of their products on a web site. Customers can put the stuff they want into an electronic basket (by clicking on a button). They then pay using a credit card, and the goods are delivered soon after. 3) Some people don’t like on-line shopping because they’re worried that their credit card details might be intercepted and used to make unauthorised purchases. Encryption software can reduce this risk. 4) Sensitive information — like credit card details — is encrypted by the web site into a code which can only be decoded with the right software and a special password called a key. In theory, only the retailer’s web site can access the information, so even if someone intercepts the transmission, they won’t be able to use the data.
Passwords give Restricted Access to some Web Sites
Some web sites restrict access to authorised users only. Schools allowing pupils and parents to access material on their intranet might do this to prevent other people accessing the information. On-line magazines also do this, so they can charge people for access.
The usual way to restrict access is to issue user names and passwords.
Get Protection from Hackers and Viruses
- Hacking means accessing a computer system and its files without permission. It’s totally illegal, and once inside a system, the hacker might be able to view, edit copy or delete important files or plant a virus. Organisations can protect themselves by using passwords, encrypting files and using hacking-detection software.
 A virus is a program deliberately written to infect a computer, and make copies of itself. They often corrupt other files — and even operating systems. They move between computer systems by attaching themselves to harmless computer files and e-mails.
A virus is a program deliberately written to infect a computer, and make copies of itself. They often corrupt other files — and even operating systems. They move between computer systems by attaching themselves to harmless computer files and e-mails.- The main way to reduce the risk of viruses is to use anti-virus software — but it’s important to use an up-to-date version because new viruses are detected practically every day.
DNS Poisoning
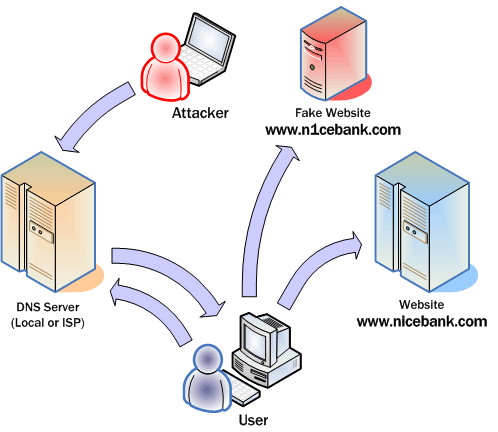
Pharming is a derivate from phishing. Phishing mean fishing ( the act of catching fish). In computer slang, fish means user name and password. Both word use “ph” instead of an “f” in this slang.
Pharming’s purpose is to obtain personal information through domain spoofingas is illustrated above. In phishing ( stealing passwords ) you are spammed with malicious e-mail requests for you to visit a malicious computer – spoof Web sites- which appear “nice and friendly sites”. Pharming on the other hand attacks a DNS server and introduces false information into the DNS server. So if you ask the server what ip matches the nicebank domain, it will send you to n1cebank.com. ( introduce your personal bank details and you are lost ).
Encryption . To alter a file using a secret code so as to be unintelligible to unauthorized parties.
Intranet: An intranet is like a private mini-Internet that can only be viewed by people connected to a particular organisation. e g a hospital might use an intranet to circulate information to its employees.
Pharming: is a hacker’s attack aiming to redirect a website’s traffic to another site.
Phishing: is the criminally fraudulent process of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details
Spoofing: A gentle satirical imitation
